Software is the intangible logic—the "brain" that directs the hardware. We must distinguish between:
Click to zoom hierarchy
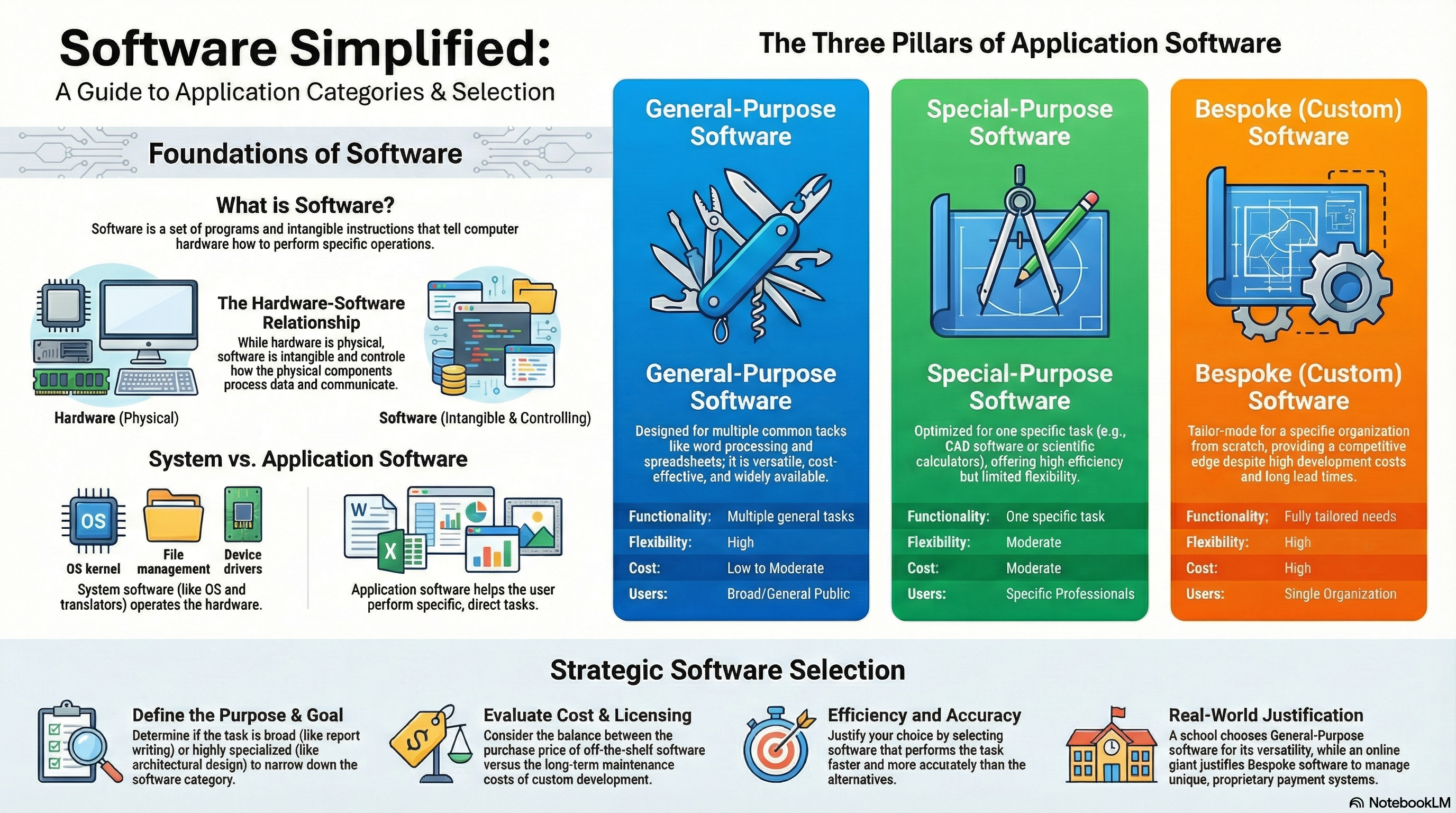
Designed for multiple, non-specific tasks. Mass-produced and versatile.
Optimized for a narrow, specific set of tasks. Used where general tools are insufficient.
Developed from scratch for ONE specific organization's unique needs.
| Feature | General-Purpose | Special-Purpose | Bespoke (Custom) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Functionality | Multiple, general tasks | Specific task only | Fully tailored |
| Flexibility | High (Multi-use) | Moderate | High (Within specs) |
| Cost | Low | Moderate | High |
| Target | Mass Market | Professionals | Specific Org |
Review the full slides for this unit:
PDF previews work best on desktop.
Open PresentationTo justify a selection, analyze: Goal, Cost, Scalability, and Precision.
Goal: Student reports & presentations.
Choice: General-Purpose.
Why: Cost-effective and versatile for many subjects.
Goal: Precise technical drawings.
Choice: Special-Purpose (CAD).
Why: Requires high precision that general tools lack.
Goal: Unique proprietary logistics.
Choice: Bespoke.
Why: Off-the-shelf cannot match unique workflow. Competitive edge.
A summary of Application Software types.